

It is considered to be "The Policeman of all Policemen", regulating the secretion of other important bodily hormones, governing the body at large and of course also the important aging process.

According to the experts, Melatonin has many vital functions in our body therefore prolonging our life span. Melatonin has strong anti-aging properties. Melatonin also shows promise as a treatment for a number of other diseases and conditions, including Hypertension, high Cholesterol, various kinds of Cancer, Autism, Epilepsy, Migraine, Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, and Alzheimer's disease. Numerous studies reveal that supplemental Melatonin can restore thymus gland function, boost immune function by increasing the production of T-cells, important to our natural defenses, and increase the body's anti-tumor activity, particularly in advanced Cancer patients. Researchers have demonstrated Melatonin's ability to treat Cancer, slow progression of AIDS, make the body more resistant to colds, and protect the immune system from the toxic effects of chemotherapy. Melatonin buffers the effects of stress and reduces the gradual decline of immunity that accompanies stress. Melatonin has been shown to be effective in victims with SAD, Seasonal Affective Disorder, which is caused by the breakdown of the circadian/body-clock rhythm. It is characterized by sleep disturbances, daytime fatigue, and reduced mental efficiency.Īccording to Patrick Quilin, Ph.D., R.D., C.N.S., Vice President of Nutrition for Cancer Treatment Centers of America: "…thirty million Americans are chronically sleep deprived … five million of these suffer from insomnia … people who sleep less than six hours each night are in poorer health and have a 70 percent higher mortality rate." Jet lag occurs in airline passengers after flights across time zones. Taking supplemental Melatonin has been shown to be an effective remedy for insomnia, shiftwork maladaptation and jet lag. What are the Benefits of Supplemental Melatonin? "Natural Melatonin" should be avoided at all costs as it may contain harmful impurities. It is identical to the naturally occurring hormone and has many benefits. Supplemental Melatonin must be synthetically produced.
TAKING MELATONIN AND FIGHTING IT FREE
Over 100 diseases have now been linked with free radical damage, including Cataracts, Macular Degeneration, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's, Arthritis, Cancer and the Aging Process itself. Antioxidants are vital to our health because they rid the body of dangerously reactive molecules called free radicals. Melatonin has been shown to be an extremely potent and wide-ranging antioxidant, protecting every part of the cell and every cell in the body, including vital brain cells. In test tube studies, Melatonin has slowed the growth of several different kinds of human Cancer cells, including breast and prostate Cancer cells. Melatonin also improves overall health when aging and relieves symptoms of SAD (Seasonal Affective Disorder). Melatonin serves many roles in our body it regulates the body clock and the secretion of other important bodily hormones, governing the aging process it enhances sleep, regulating the bodies internal clock and counteracts insomnia and jet lag, boosts the immune system, acts as an antioxidant to fight free radicals, improves mental deficiency in Alzheimer's disease, improves joint function in arthritis and influences the reproductive and cardiovascular systems. The levels of Melatonin produced by the pineal gland are abundant in children, peak slightly before puberty, and decrease steadily thereafter into old age. As we get older, the pineal gland rapidly wears out, due to an excessive build up of calcium, which is known as calcification. The risk of overdosing Melatonin is therefore minimal. It is both a fat- and water- soluble hormone. Melatonin is rapidly metabolized, chiefly in the liver and it is excreted in the urine. The secretion of Melatonin peaks in puberty, after which it rapidly decreases, and very often people over 50 secret only one tenth of the of the amount secreted in puberty. For this reason Melatonin has also been called "the Hormone of Darkness". The synthesis and release of Melatonin is inhibited by light. The secretion of Melatonin occurs during the night, as a response to darkness, and it peaks in the middle of the night, and then gradually falls during the second half of the night.
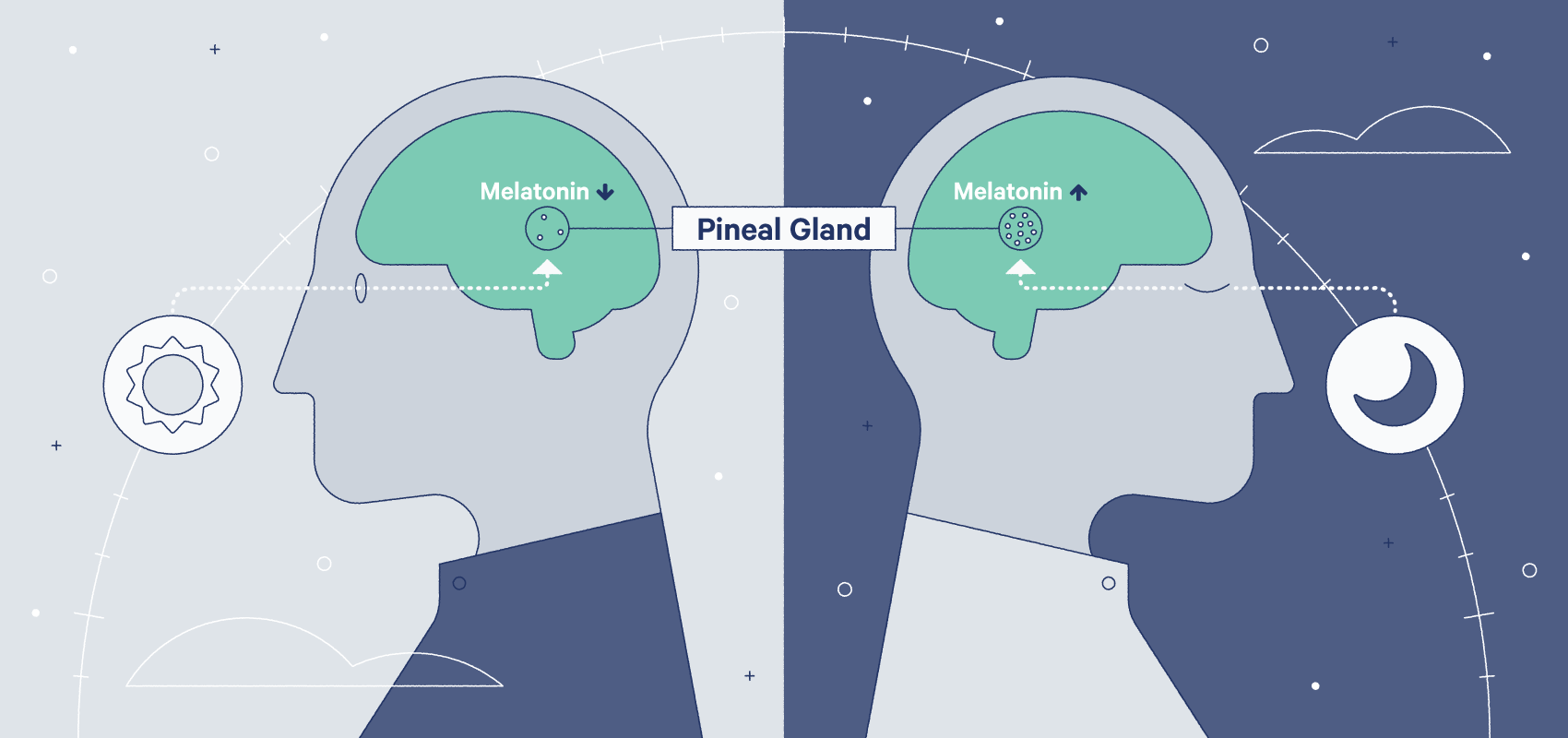
In humans, it is produced mainly by the pineal gland, a gland about the size of a pea, which is located in the center of the brain, but also in the stomach and in the eye. Melatonin is a hormone like substance that is found in all forms of life on earth.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
